Same-Day Delivery Available! Order before 4 PM and get your auto parts delivered the same day. For customers within Accra, we also offer instant delivery within 30 minutes–3 hours. Fast. Reliable. Right to your doorstep.
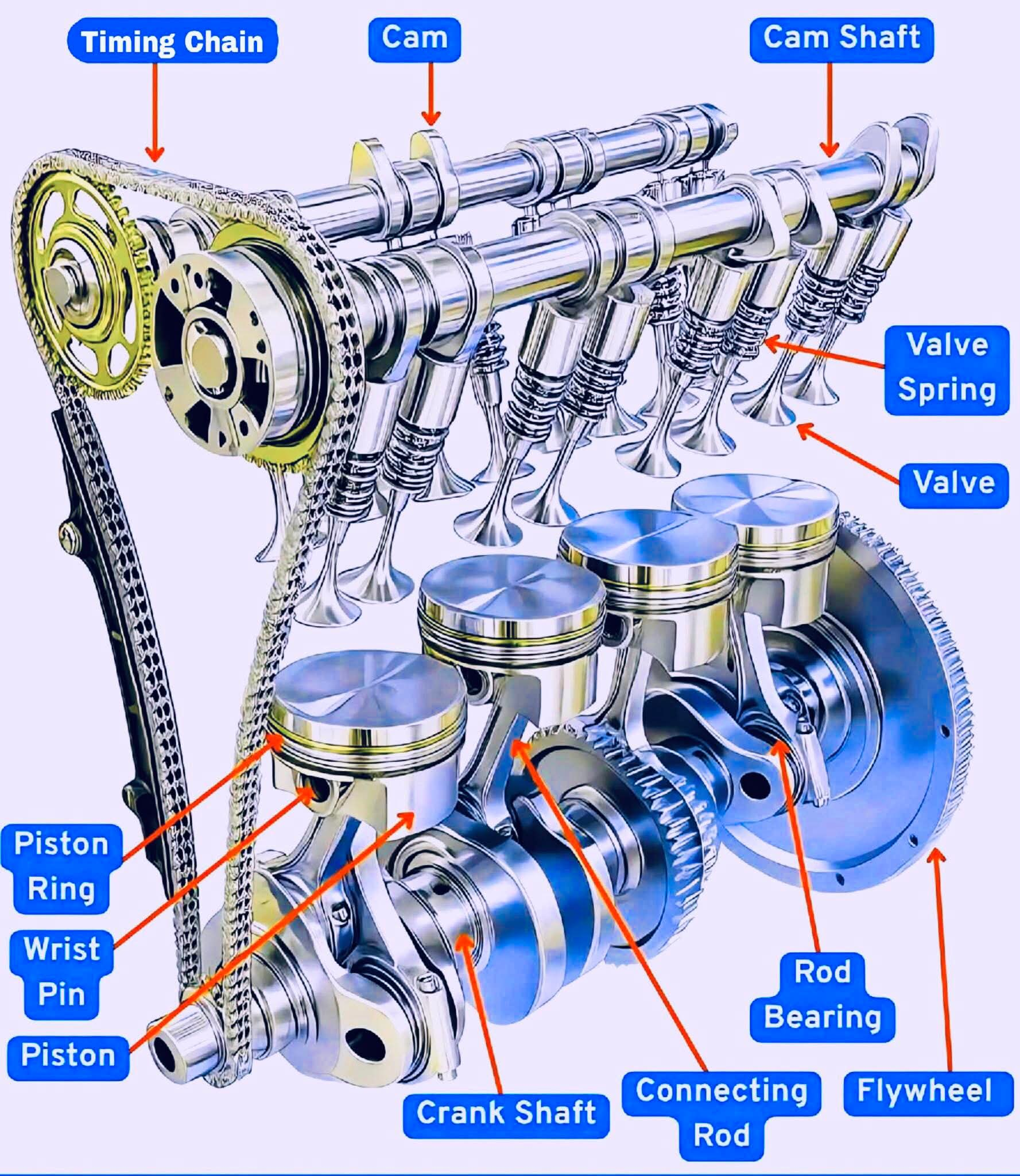
Understanding Your Car’s Engine: Key Internal Components
Your car’s engine may look complicated, but at its core, it’s a set of carefully designed parts working together to create power. Here’s a simple guide to the most important internal engine components:
---
1. Engine Block
The “body” of the engine. It holds the cylinders and supports most of the other engine parts.
---
2. Cylinders
Hollow spaces inside the engine block where fuel burns. The number of cylinders (4, 6, or 8) often tells you how powerful the engine is.
---
3. Pistons
Small moving parts inside the cylinders that go up and down when fuel burns. They’re the engine’s muscle, turning fuel into motion.
---
4. Piston Rings
Thin rings around each piston. They seal the cylinder so fuel doesn’t leak and control oil use.
---
5. Connecting Rods
Strong metal arms that connect the pistons to the crankshaft.
---
6. Crankshaft
A long shaft at the bottom of the engine. It turns the piston’s up-and-down movement into spinning power that drives the car.
---
7. Cylinder Head
The “lid” on top of the engine block. It houses valves and spark plugs, helping fuel burn efficiently.
---
8. Valves
Intake valves let air and fuel into the cylinder.
Exhaust valves release the burnt gases.
---
9. Camshaft
Controls the opening and closing of the valves in perfect timing with the crankshaft.
---
10. Timing Belt/Chain
Keeps the crankshaft and camshaft moving together in sync.
---
11. Spark Plugs (Petrol Engines)
Create a small spark to ignite the air-fuel mixture and start combustion.
(Diesel engines use glow plugs to help start in cold conditions.)
---
12. Fuel Injectors
Spray the right amount of fuel into the engine for burning. Modern engines use injectors instead of carburetors.
---
13. Oil Pump
Moves engine oil around to keep everything lubricated and prevent damage.
---
14. Water Pump
Keeps coolant moving through the engine to stop overheating.
---
15. Flywheel
A heavy wheel attached to the crankshaft that helps keep the engine running smoothly.
---
🚗 In short: These components work together in four steps—intake, compression, power, and exhaust—to create the energy that moves your car.